TRANSPORT, MINING AND BUILDING MACHINERY ENGINEERING
Introduction. At the heart of the creation and improvement of robotic road construction machines and complexes are mathematical modelling methods, the use of which is justified both in the development of the machines themselves and mathematical models that describe the turning processes and determine the movement of the machine along a given trajectory.
The method of research. The article presents a generalized design scheme for the rotation of a three-axle road roller, which reflects its main geometric and kinematic characteristics. On the basis of the design scheme, a mathematical model of the rotation of the skating rink was compiled. As a result of the developed mathematical model, a program code was built in the MATLAB software product, which formed the basis of theoretical studies that made it possible to fully study the influence of the design and operational parameters of the machine on the motion trajectory and positioning accuracy.
Results. The calculated dependencies have been obtained to determine the influence of such parameters as the speed of the road roller, the angular speed of the drum rotation on the distance of rebuilding on a parallel course and on the displacement of the rotary drum, that is, on the trajectory and positioning accuracy of the road-building machine.
Conclusion. On the basis of the design scheme, a mathematical model of the rotation of the roller was compiled, as a result of which studies were carried out aimed at studying the influence of the design and operational parameters of the machine on the trajectory of the road roller and the accuracy of its positioning on the construction site when performing technological operations.
Introduction. At the beginning of the production of road construction works, it is necessary to remove stones, bushes, trees from the right-of-way of the future road. To perform such work, it is advisable to use cyclic units, in particular, with bulldozer equipment. Interaction with the soil of the knife and the blade of the bulldozer is accompanied by a complex of interrelated processes. These processes complicate the theoretical analysis of the interaction of the knife and the bottom part of the blade of bulldozer equipment with the soil. Therefore, despite the large number of publications, the interaction of the knife and the bottom part of the blade of bulldozer equipment with the soil is not analyzed in sufficient details. Meanwhile, without a detailed analysis of this interaction, it is difficult to modernize bulldozer equipment.
The method of research. Interaction with the soil of the knife and the blade of the bulldozer has two features. First, the knife of a bulldozer with a straight blade is installed perpendicular to the direction of movement of the unit, so the bulldozer knife carries out energy-intensive cutting of the soil. Secondly, the cut layer of soil moves the pile of the bulldozer in front of it. The concave shape of the surface of the working body causes a concave mapping of crumple stresses, leading to the appearance of a zone of volumetric compression of the soil, which increases more and more during the movement of the unit. Both the deviator and ball components of the stress tensor in the ground increase. Therefore, the front surface of the knife is divided into a blade and a plane that carries out, together with the plane of the lower part of the blade, the displacement of the primary displaced soil. It is necessary to consider separately the impact on the ground of the blade, the edge of the knife and the front surface of the knife and the lower part of the blade.
Results. From the drawings the length of the trace of the surface of the pseudo-displacement of the soil in the longitudinal-vertical section, the area of the primary ground shift with the edge of the knife, the area of impact on the ground of the knife surface, the area of impact on the ground of the surface of the lower part of the blade are determined. The area of pseudo-displacement of the soil and the area of displacement of the primary shifted soil were calculated. The dependencies of the areas on the recess of the bulldozer knife are constructed.
Conclusion. As the depth of the bulldozer knife increases, the area of pseudo-displacement of the soil by the surface of the knife, the area of primary ground shear with the right or left edge of the knife increases linearly. In this case, the displacement area of the primary shifted soil increases by the parabola. Identifying the area of the pseudo-displacement of the soil, the area of the primary ground shift with the right or left edge of the knife and the displacement area of the primary shifted soil will determine the energy costs required to affect the surface of the knife and the lower part of the blade on the ground.
TRANSPORT
Introduction. Public transport in the life of modern cities plays a significant role in the formation of urban transport systems, thereby affecting the environment, the quality of people’s life, their health, road safety, etc.
Knowledge of the existing features of public transport functioning will allow for competent intervention in the operation of this system, increase its attractiveness and attract additional passengers. It is possible to obtain such knowledge by polling system users – passengers. Transport surveys around the world are widely used to develop measures to improve the operation of transport, as well as to evaluate their effectiveness.
This article provides an analysis of the regulatory documents governing the conduct of transport surveys, as well as scientific literature, including foreign ones, describing both the conduct and results of such surveys. The relevance of the topic is due to the need to generalize the experience of conducting transport surveys and the implementation of the obtained quintessence when questioning passengers in the Republic of Belarus. Tasks to be solved:
– analysis of the legislation of the Republic of Belarus on the subject of the study;
– analysis of the experience of conducting transport surveys abroad;
– development of general recommendations for the structure, content and method of carrying out a transport survey;
– development and placement of a questionnaire for users to fill out.
The purpose of the work is to develop the structure, content and method of conducting a transport survey of passengers in the cities of the Republic of Belarus, taking into account the current legislation of the country and the experience of implementing such events in foreign countries.
Scientific novelty lies in the use of scientific methods of analysis and synthesis in the development of the structure and content of the transport survey.
Materials and methods. When writing the article, analysis and synthesis scientific methods were used.
Results. Based on the results of the article, the structure of the transport survey and methods for conducting it for the conditions of the Republic of Belarus were developed.
Discussion and Conclusions. The obtained structure of the transport survey and the method of its conduct correspond to the conditions for the functioning of the urban passenger transport of the Republic of Belarus and allow obtaining initial information to substantiate the ways of further development of this type of transport.
Introduction. In the economy of states, one of the constant tasks remains to ensure the urgent needs of the population, in an autumn-winter period in cities and settlements, the task of providing fuel (coal) to households is highlighted. The demand for coal is limited by solvency and distributed over the entire period of negative air temperatures. Hence, the supply of coal for the period of heating of dwellings is formed, in many cases, by purchasing lots of coal, representing a share of the total demand during the specified period. The purpose of this work is to find reasonable answers on the use of transportation technologies for limited shipments of goods in cities.
Materials and methods. The solution to the problem was carried out within the framework of operational planning for the transportation of limited shipments of coal for the population throughout the city on the basis of the concept of an approach to building a general theory of truck systems functioning for motor transport shipping network, using a regulatory approach when calculating transportation costs, descriptive models of the car’s operation in micro- and delivery motor transport shipping network.
Results. Through mathematical modelling, reasonable values of operational plans for the transportation of limited shipments of coal in cities by machine technology and delivery were obtained. Regulatory approach to cost calculation, electronic database of road transport industry updated at the date of calculation. Software and mathematical support for calculating the costs of cargo transportation as part of models of micro and especially small motor transport systems made it possible to reliably determine the planned values of transportation costs by machine technology and delivery.
Discussion and conclusion. The advantage of using delivery technology in the conditions under consideration has been established, when transporting coal by road using the case of a city.
Introduction. Current methods for determining passenger ridership, due to their complexity and limited efficiency, do not allow monitoring transport demand at the proper level (in terms of comprehensiveness and continuity). Nowadays, technologies based on the collection, integration and analysis of big data (Urban computing, Big data, Internet of things) are used to create effective solutions in many aspects of our lives (including for urban transit).
Materials and methods. Within the framework of this approach, a methodology for determining the correspondence of transit passengers from the operations of validating any kind of electronic travel tickets: smart cards, transport cards, magnetic cards has been developed. Each operations details are recorded in the Automated Fare Collection (AFC) system during the validation.
This methodology based on the definition and evaluation the set of acceptable options of passenger trips sequences, which form the passenger correspondence, taking into account many factors that effect on the route choice by a passenger. For example, in contrast to previous studies, the practice of paying for trip at any point on the route, not necessarily immediately after boarding the vehicle, was taken into account.
Results. It was proved that passenger correspondence calculated using the developed methodology statistically corresponds to the general set of transit passenger ridership within acceptable errors. The chaacteristics of transit demand is provided in the results.
Discussion and conclusion. The application of the developed methodology makes it possible to organize continuous monitoring of passenger flows, technical and operational indicators of the functioning of transit system and thus implement the concept of sustainable development of public transport by designing public transit supply that meets demand.
Introduction. The existing methodology for determining quantitative indicators of training specialists for motor transport complexes of the regions, taking into account the technological needs of economic entities, does not reflect the rules for the formation of structural characteristics of security in specialists and staff of motor transport. This methodology needs to be further developed to identify structural indicators of the human resources system. The main indicator of this structure is the ratio of the number of specialists by training levels. This article fills the gap and aims to improve the structural indicators of the training of motor transport specialists and staff. This is due to the relevance of developing an appropriate methodology.
Materials and methods. Classical methods of analysis, synthesis, structural modelling, provisions of the theory of motor vehicles maintenance, methods of mathematical analysis and fundamentals of algorithms are used in the work. The obtained results are applicable for their use in improving specialists and staff training in organisations and enterprises of motor transport, regardless of their departmental subordination.
Results. The main result of the work is a methodology for determining the structure of specialists skilled in motor transport in the region, differing from the known ones that it takes into account the distribution of the number of the skilled staff according to the levels of vocational higher and secondary education between motor transport and car service enterprises, regardless of the departmental subordination. The method of structural ranking of the specialists skilled in motor transport enterprise management has been developed. These results represent the scientific novelty of the study. The results of the structural distribution of specialists by levels of education have been determined, the corresponding algorithm has been developed.
Discussion and conclusions. A methodological tool for determining the structure of specialists with motor transport education in the region has been developed. The application of the results of the work will make it possible to increase the validity of the state task to improve the training of specialists and motor transport staff in the regions.
CONSTRUCTION AND ARCHITECTURE
Introduction. An analysis of the literature and experimental data on the resource provision of the construction market has shown that the development of new and effective materials with improved quality parameters is an urgent task, and in the long term will serve as an impetus for the development of the building materials market. Currently, the peat industry in Russia is experiencing a serious decline in the extraction of peat raw materials, the reserves of which are practically inexhaustible. One of the possible ways to develop this industry in the Tomsk region can be the organisation of the production of competitive structural, heat-insulating and heat-insulating materials using local raw materials, namely lowland peat and vermiculite, which will improve the economic prestige of the region, create new enterprises and jobs.
Materials and methods. The studies using the methods and tests set out in national standards were carried out. The measurement of the obtained material density was carried out in accordance with GOST 17177-94. The determination of the samples strength in compression and in bending was carried out in accordance with GOST 23789-2018. The determination of the moisture content percentage of the samples was carried out in accordance with GOST 23789-2018.
Results. The results of the research made it possible to determine the basic requirements for the designed composition of lightweight concrete based on gypsum binders and peat vermiculite granules. The relationship between the strength characteristics and density of lightweight concrete has been studied, it has been established that at average density values in the range of 530-850 kg/m3, the resulting material meets the basic technical requirements of heat-insulating lightweight concrete (GOST 25820-2014).
Discussion and conclusions. In the work, experimental studies determined the rational ratio of the components of lightweight concrete based on gypsum binder and peat vermiculite granules, at which the maximum value of their strength is achieved at a minimum average density. Based on the data obtained, it was found that in order to achieve the necessary physical and mechanical properties of lightweight concretes based on gypsum binders, the optimal size of peat-vermiculite granules should be no more than 5 mm.
Introduction. Increasing the durability of road structures and extending the construction season for the installation of monolithic road pavements are urgent tasks. Non-rigid road pavements are of particular interest. Replacing the bases of granular materials (crushed stone, gravel, etc.) with monolithic ones reduces the material consumption of the road surface by 20-50%, the cost of construction works by up to 45% and increases the service life of roads by 1.5-2 times. The extension of the construction season for the installation of monolithic bases contributes to an increase in the pace of construction, a more rational use of road construction equipment, securing highly qualified specialists at the enterprise and reducing overhead costs. A multi-tonnage waste having independent binding properties is of particular interest, for example, belite sludge of alumina production. The article is devoted to a comprehensive study of the physical mechanical and technological properties of natural belite sludge in order to use it for the making of monolithic layers of road and airfield pavement in winter, without the introduction of antifreeze additives.
Materials and methods. The freezing temperature of the belite sludge of minus 2 ° C was determined by the thermoelectric method. Its compactibility in the range of negative temperatures, the ability to restore the destroyed structure after re-compaction, the regularities of cooling of the material during technological operations for the construction of structural layers in winter are studied. The compaction was studied by pressing samples from sludge of optimal humidity, at its temperatures from 20 to minus 10°C. The study of the processes of structure formation of sludge and sludge crushed stone materials consisted in studying the kinetics of hardening of samples stored in climatic chambers that simulate changes in average monthly air temperatures in an annual cycle (from 20°C to minus 20°C) and in natural conditions (outdoors). In parallel, thermographic and electron microscopic studies of neoplasms in the hardening material were performed. To study the regularities of the cooling of the sludge layers, a laboratory experiment was conducted that simulates two-way (top and bottom) freezing of the material in a climatic chamber at temperatures of minus 10, minus 15 and minus 25°C.
Results. A complex of unique physical chemical and technological properties of natural belite sludge has been identified, which consist in maintaining the initial density and activity after freezing, the ability of sludge and sludge crushed stone materials to harden at negative temperatures, a reduced freezing temperature of minus 2°C, good compaction in the range of negative temperatures (up to minus 6°C). The temperature and technological parameters of the sludge preparation for the production of works in winter are investigated. The regularities of sludge cooling in the technological process for the construction of structural layers in winter are studied. A technology has been developed for the making of monolithic layers of the road pavement made of belite sludge and crushed stone materials at negative air temperatures up to minus 20°C. The practical experience of the belite sludge use in the construction of roads in 2-4 road-climatic zones is summarized.
Introduction. The purpose of the article is to determine the influence of the steel fiber profile and the composition of the matrix on their adhesion in dispersed reinforced concrete.
Materials and methods. Studies have been carried out using the test methods set out in national standards. To determine the characteristics of the adhesion strength of fibers with a matrix, an original technique developed at SPbGASU was used.
Results. The degree of influence of the geometric shape of steel fibers – anchor and wave profile on the adhesion strength characteristic is determined. The adhesion strength of steel fiber with cement and concrete matrix was assessed (Cement: Sand = 1:1, Cement: Sand = 1:2 and Cement: Sand = 1:3). The influence of the volume fraction of the cement paste on the characteristic of the adhesion strength of the steel fiber with the matrix has been experimentally proven.
Conclusions. The experimental data obtained confirm the effectiveness of dispersed reinforcement through the use of anchor fibers in combination with a rationally selected composition of the concrete matrix.
Introduction. An assessment of the influence for the type of bonds and the magnitude of the prestress of the longitudinal working reinforcement on the stress-strain state of the reinforced concrete floor slab, developed by the authors was made.
Materials and methods. The studies on a finite element model of a reinforced concrete floor slab, implemented in LIRA software package were carried out.
Results. The development of stress values and transverse vertical displacements directly depended on the support conditions of the floor slab.
Limitation of transverse horizontal displacements on the support by any of the selected methods made it possible to reduce 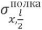 stresses by 3.47 - 3.78 times,
stresses by 3.47 - 3.78 times, 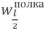 deflections by 1.5 - 1.52 times,
deflections by 1.5 - 1.52 times, 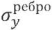 stresses - up to 11.9 times, wребро deflections - 1.18–1.53 times.
stresses - up to 11.9 times, wребро deflections - 1.18–1.53 times.
Creating an end rib or limiting movement with an additional horizontal connection had almost the same effect.
The transverse horizontal displacements of the lower face of the longitudinal contour rib in the direction of the 𝑢ребро span which occurred in the floor slab, which did not have an end rib and limitation of displacements in the transverse direction, were in a parabolic relationship with the magnitudes of the vertical transverse forces.
In a florr slab with limited displacements in the transverse direction or with an end rib, 𝑢ребро displacements were 3.88–4.32 times less, and at the ends they depended on the deformability of the bonds, i.e. when horizontal movement was prohibited, they were equal to zero.
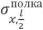 stresses acting on the lower edge of the flange in the transverse direction, in the region of the middle of the span in the floor slab with reinforcement prestressed to the maximum value, had positive values almost over the entire width of the flange and directly depended on the thickness of the slab in each section.
stresses acting on the lower edge of the flange in the transverse direction, in the region of the middle of the span in the floor slab with reinforcement prestressed to the maximum value, had positive values almost over the entire width of the flange and directly depended on the thickness of the slab in each section.
Prestressing made it possible to reduce 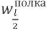 deflections by 4.02 - 4.37 times, wребро deflections by 1.09 - 5.59 times, and evenly distribute
deflections by 4.02 - 4.37 times, wребро deflections by 1.09 - 5.59 times, and evenly distribute 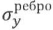 stresses along the length of the longitudinal contour rib, to make they are only tensile, close to zero along its entire length.
stresses along the length of the longitudinal contour rib, to make they are only tensile, close to zero along its entire length.
The prestressing of the reinforcement of the maximum value made it possible to increase the horizontal rigidity of the longitudinal contour rib of the floor slab and limit its transverse 𝑢ребро movements.
The transverse displacements that occurred near the support of the prestressed shell slab were 1.04 - 1.2 times less than in the shell slab with non-stressed reinforcement, on the rest of the span - slightly more, changing evenly, without sharp changes, unlike floor slabs with non-stressed reinforcement.
Discussion and conclusion. It is established that the optimal design of the floor slab under the study should have restrictions on the movements of the supports and the maximum possible prestressing of the longitudinal working reinforcement.
The practical significance of the study is that the specified reference conditions and prestress allow maximum deformation resistance of the structure, which in our case directly affects the bearing capacity of the slab.
ISSN 2658-5626 (Online)










































